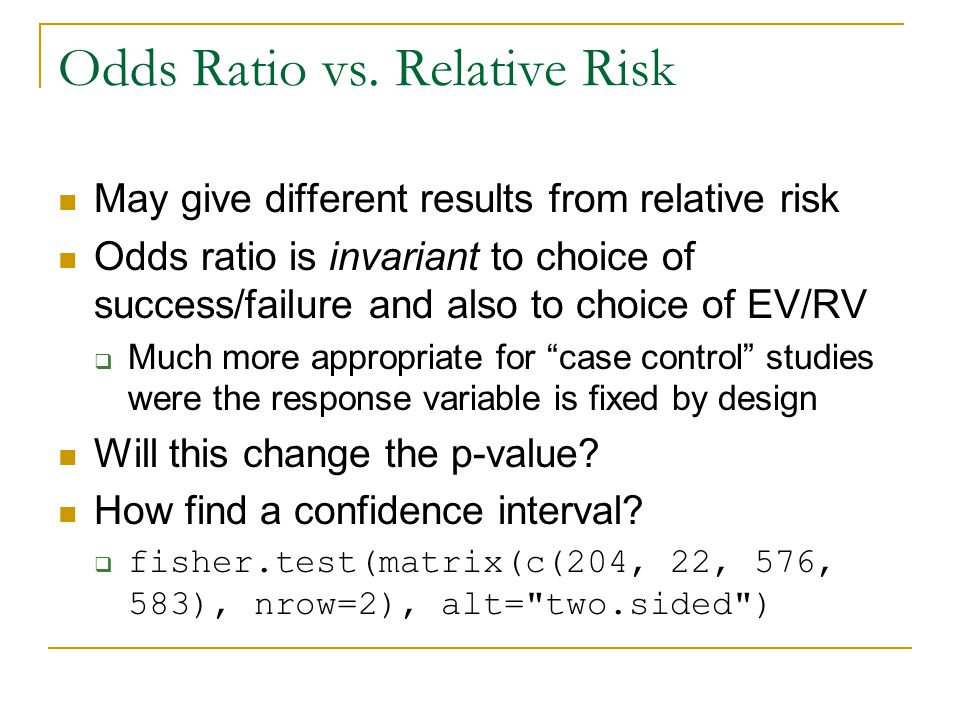
Odds Ratio vs Relative Risk What's the Difference?Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group

Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data
Odds vs relative risk
Odds vs relative risk-Since relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effectiveness, the distinction is important especially in cases of medium to high probabilities If action A carries a risk of 999% and action B a risk of 990% then the relative risk is just over 1, while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds with BThe relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks is




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds ratio relative risk Relative risk An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Relative risk isThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control groupThe difference between odds ration and relative risk is that the relative risk is a ration of two ideal properties while the odds ratio is mainly concerned about the specific ratio of two different odds This is because, the relative risk is often used to refer the proportion of people with a particular risk factor who have that risk factor
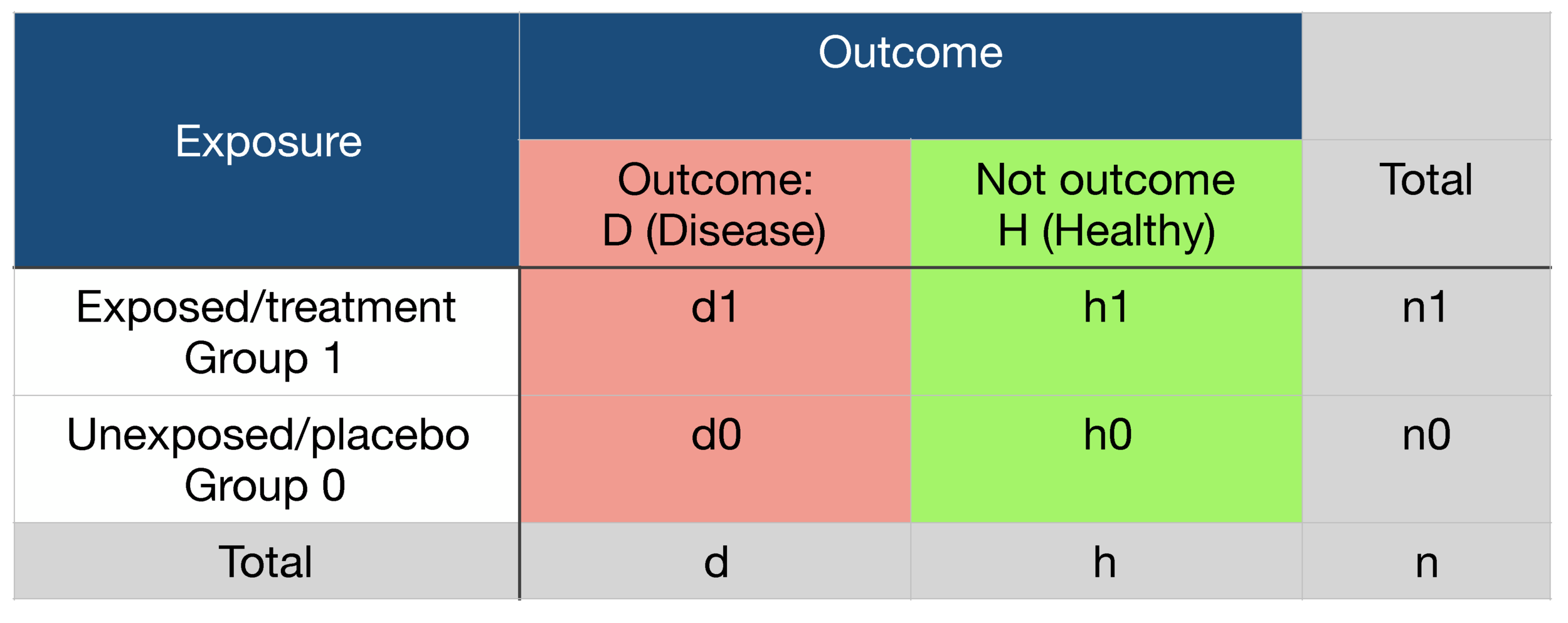
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatmentRelative Risk Relative risk is a ratio of the risks of two groups In the example described above, it would be the risk of heart attack for a person in their current condition compared to the risk of heart attack if that person were in the normal ranges However, to truly interpret the severity of a relative risk we have to know the baseline risk
Risk is often a more intuitive concept than odds, and thus understanding relative risks is often preferred to understanding relative odds However, OR does not suffer from the same causal assumption limitations as RR, making it more widely applicablePortantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcomeRelative risk is the ratio of the risks for an event for the exposure group to the risks for the nonexposure group



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Odds Chegg Com
You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audienceThe relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program




First Aid Epidemiology Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research
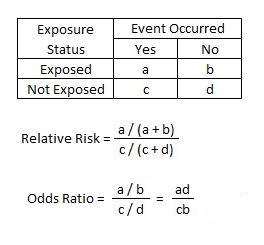
Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Attack Rate (Risk) Attack rate for exposed = a ⁄ ab Attack rate for unexposed = c ⁄ cd For this example Risk of tuberculosis among East wing residents = 28 ⁄ 157 = 0178 = 178% Risk of tuberculosis among West wing residents = 4 ⁄ 137 = 0029 = 29% The risk ratio is simply the ratio of these two risks Risk ratio = 178 ⁄ 29 = 61



Relative Risk Article



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
If odds are stated as an A to B chance of winning then the probability of winning is given as P W = A / (A B) while the probability of losing is given as P L = B / (A B) What does Relative Risk tell you?2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter



1



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id



2




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



1




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Github Flor3652 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Shiny App




Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Statistical Notes For Clinical Researchers Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Jussi Tervola در توییتر Nice Graph Depicting The Relationship Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk T Co Lssoq7tqmd



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



bestpictnjne 人気ダウンロード Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk When To Use Should I Use Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Relative Risk Bicim




Relative Risk Analysis And Odds Ratio Analysis



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining
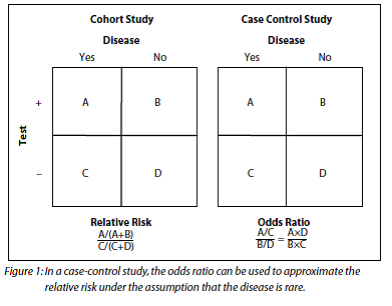



Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
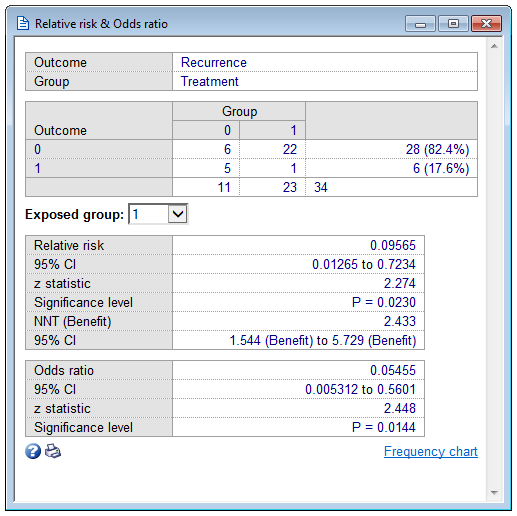



Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead Abstract Europe Pmc




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
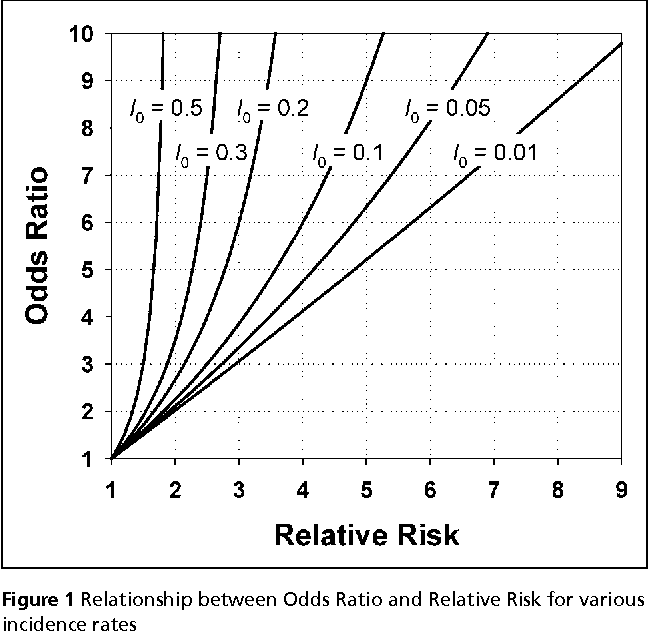



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Relative And Atribute Risk




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Free Medical Videos




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
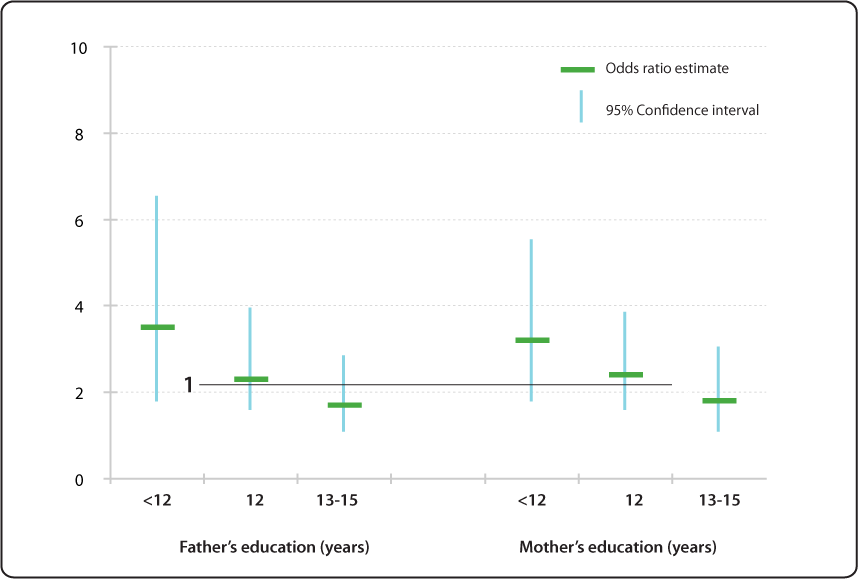



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
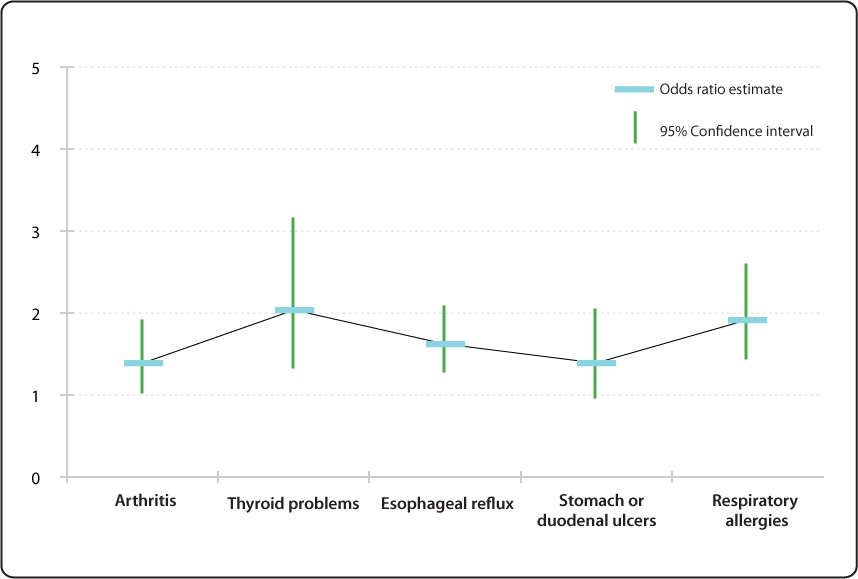



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Categorical Data And Chi Square Tests Biostatistics For The Health Sciences




Solved Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com



Odds




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Data Are Still Portrayed With Inappropriate Scales In The Medical Literature Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Or2rr



2




Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Calculating Atrium




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




16 Odds Ratios From Casecontrol Studies Casecontrol Studies
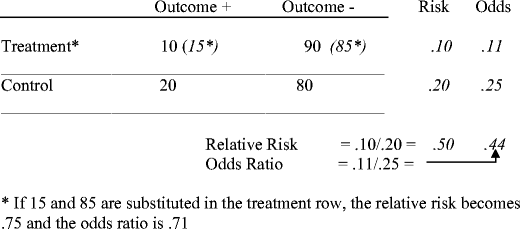



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Risk Differences Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Plots With Proc Freq




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download



1




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data
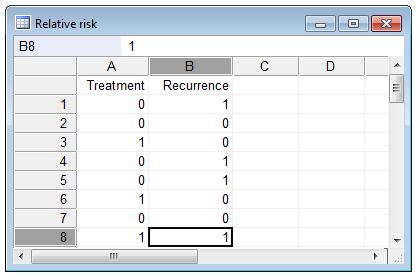



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Kevin Whelan No Twitter If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Literature Search



2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Critical Numbers Living With Risk At The End




7 Stats Ideas Research Methods Statistics Math Nursing Research



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿