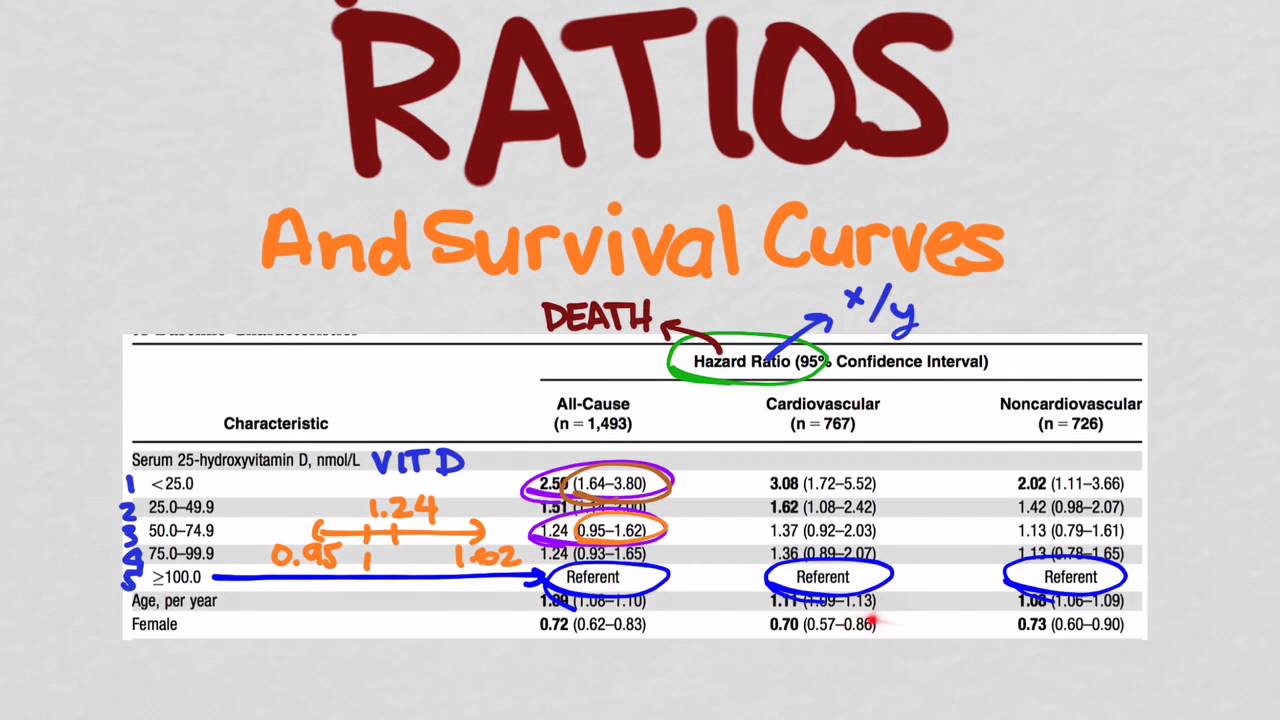
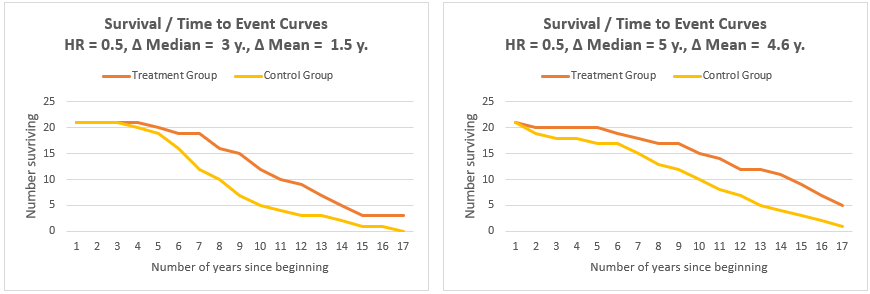
May 03, · In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data Under proportional hazards it is probably "natural" to thinkThe hazard ratio is simply the value of the hazard calculated from the treatment curve, divided by the hazard calculated from the control curve Based on the complexity, statistical software is required to make this calculation to estimate the hazard ratio Figure 1 The timetoevent curve or KaplinMeier curve

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Risk ratio vs odds ratio interpretation
Risk ratio vs odds ratio interpretation-The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for males Now we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regressionInterpretation of a Hazard Ratio HR (E vs C) = 075 for an overall survival end point This means on average, under an exponential distribution, approximately • a 25% lower risk of death (25% as 1
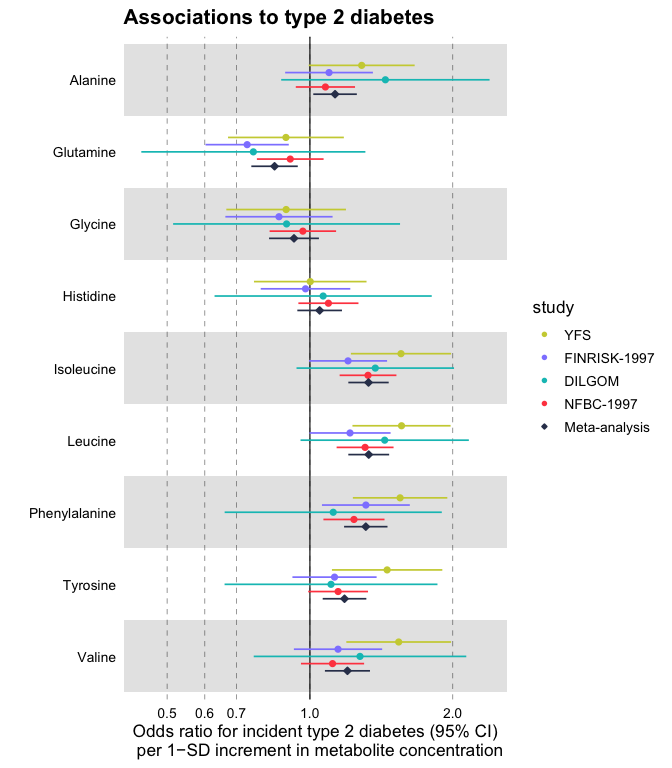


Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot
HR > 1 increase in the hazard;This video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratiosJun 01, 11 · Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column ( c ) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)
Start studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probabilityMay 14, 19 · L'Odds Ratio (OR) est le rapport des cotes d'exposition Cette notion de cote est semblable à celle utilisée pour les paris sportifs Dans notre exemple la cote chez les personnes exposées est de 30 contre 70 Chez les non exposés, cette cote est de 10 pour 90
May 18, 12 · However, you can calculate an odds ratio and interpret it as an approximation of the risk ratio, particularly when the disease is uncommon in the population Exercise 38 Calculate the odds ratio for the tuberculosis data in Table 312 Would you say that your odds ratio is an accurate approximation of the risk ratio?Hazard ratio, odds, and probability of healing There is an alternative interpretation of the hazard ratio that may be intuitively easier to understand The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint firstDec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;


Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad
Feb 12, 12 · "When you are interpreting an odds ratio (or any ratio for that matter), it is often helpful to look at how much it deviates from 1 So, for example, an odds ratio of 075 means that in one group the outcome is 25% less likely An odds ratio of 133 means that in one group the outcome is 33% more likely"An odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictorSquare statistic in unstratified analysis and in the MantelHaenszel odds ratio in stratified analysis 3, Section 14 and in the logistic model of multivariate analyses 4,5 Odds ratios also provide a connection between analyses of data from cohort and case referent studies However, because of



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
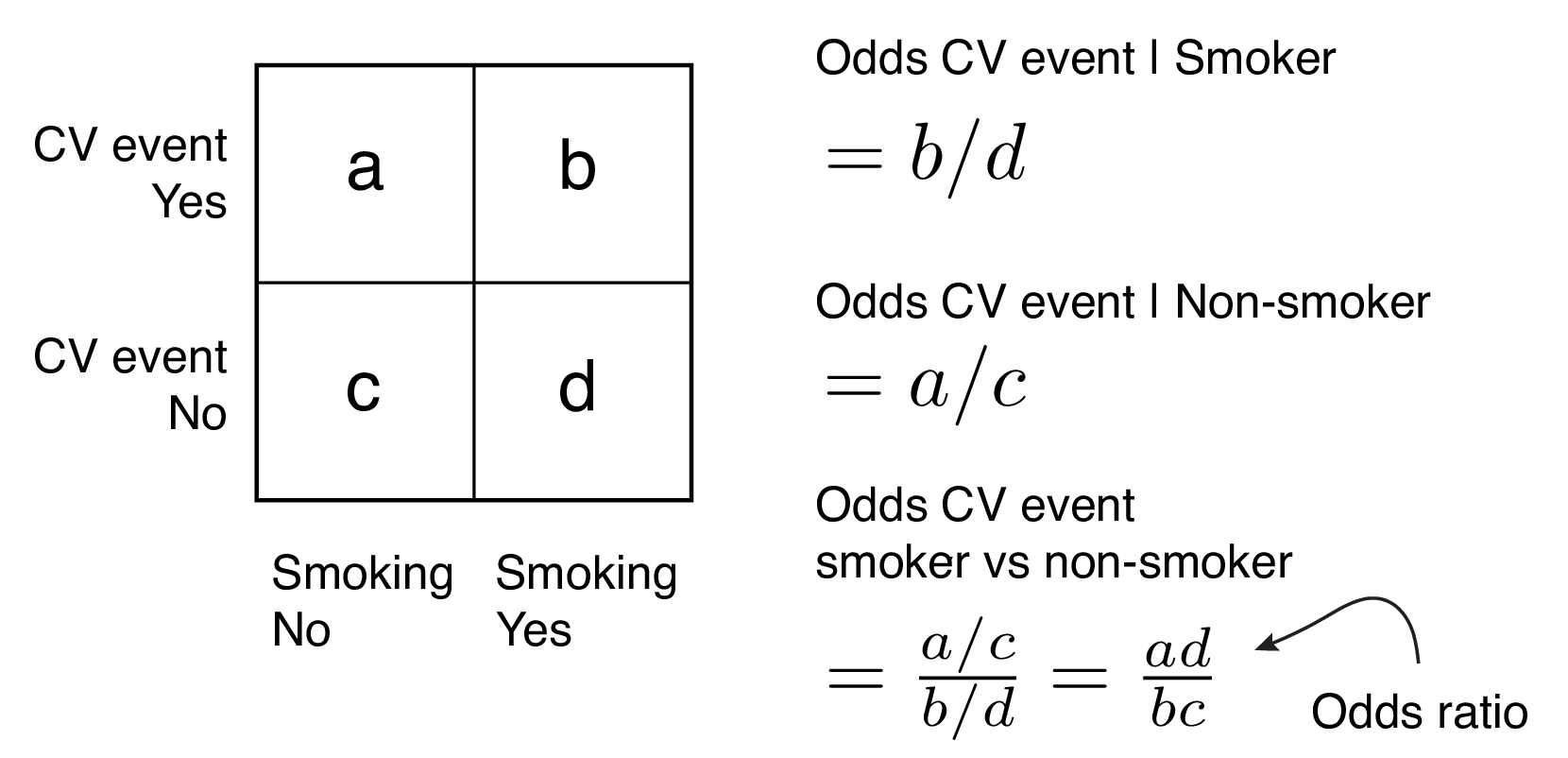
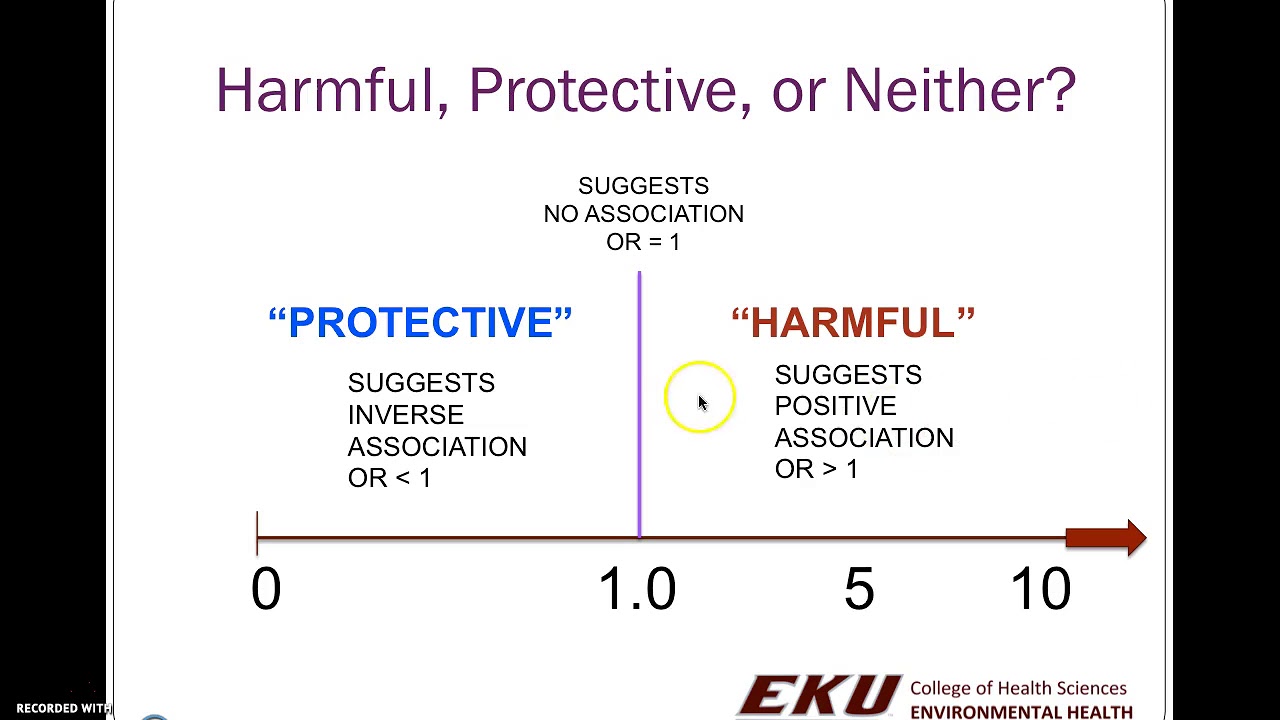
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Jun 01, 12 · Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XJan 11, 18 · Step 2 Finally, we calculate the ratios of these two odds and interpret the differential effect of exposures in those two groups OR = a / c / b / d = ad / bc Interpretation of Odds Ratio As we already mentioned elsewhere, Odds ratio is utilized to assess the strengths of association between exposure and the outcome In our hypothetical



Challenges In The Design And Interpretation Of Noninferiority Trials Insights From Recent Stent Trials Sciencedirect


Lesson 13 Proportional Hazards Regression Stat 507
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalWhat we model (log) Hazard rate (log) Odds h(t) = lim 4!0 P(t T95% confidence interval, 025 to 047;



The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
A logrank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing timetoevent data gives rise to something in between The appropriate effect measure should beAug 01, · Hazard ratio Similar to how odds is used in logistic regression, the equivalent for odds in cox proportional hazard model is hazard The hazard ratio look into comparing the hazards occurring in"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two



Is There A Way Of Representing The Hazard Ratios Graphically After Cox Regression Analysis In Stata



Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Apr 05, 16 · Interpretation of Hazard Ratio HR = 05 at any particular time, half as many patients in the treatment group are experiencing an event compared to the control group HR = 2 at any particular time, twice as many patients in the treatment group are experiencing an event compared to the control groupNelsonlen cumulative hazard estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 100 0 300 400 group 0 group 1 Hazard Ratio = 71 KaplanMeier survival estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 025 050 075 100 group 0 group 1 Title Point Estimation Odds Ratios, Hazard Ratios/Rates, Risk Differences,Precision AuthorWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR



The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Jul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programHR < 1 reduction in the hazard Moving again on the R code, we can see (by means of the summary function) the hazard ratios for the covariates included in the modelFeb 24, 13 · Odds ratio 1 ODDS Chance of event occurring divided by chance of event not occurring › For example, in 100 births, the probability of a delivery being a boy is 51% and being a girl is 49% › The odds of a delivery being a boy is 51/49 = 104 In simpler term, an odds of an event can be calculated as Number of events divided by number of nonevents
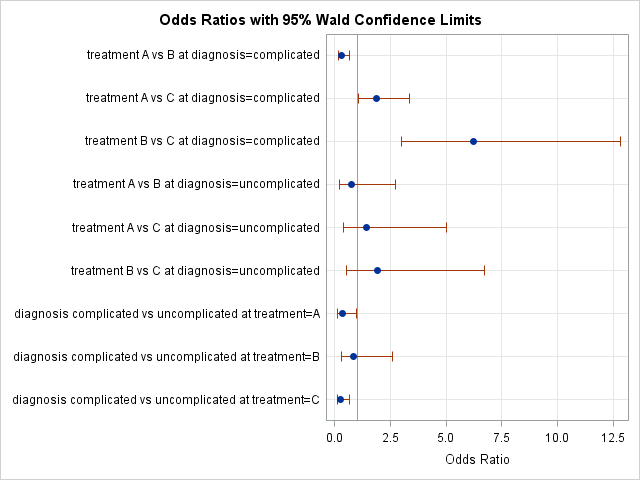


Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop
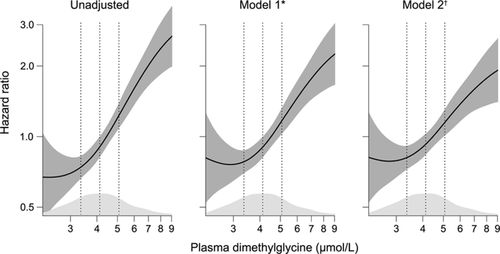


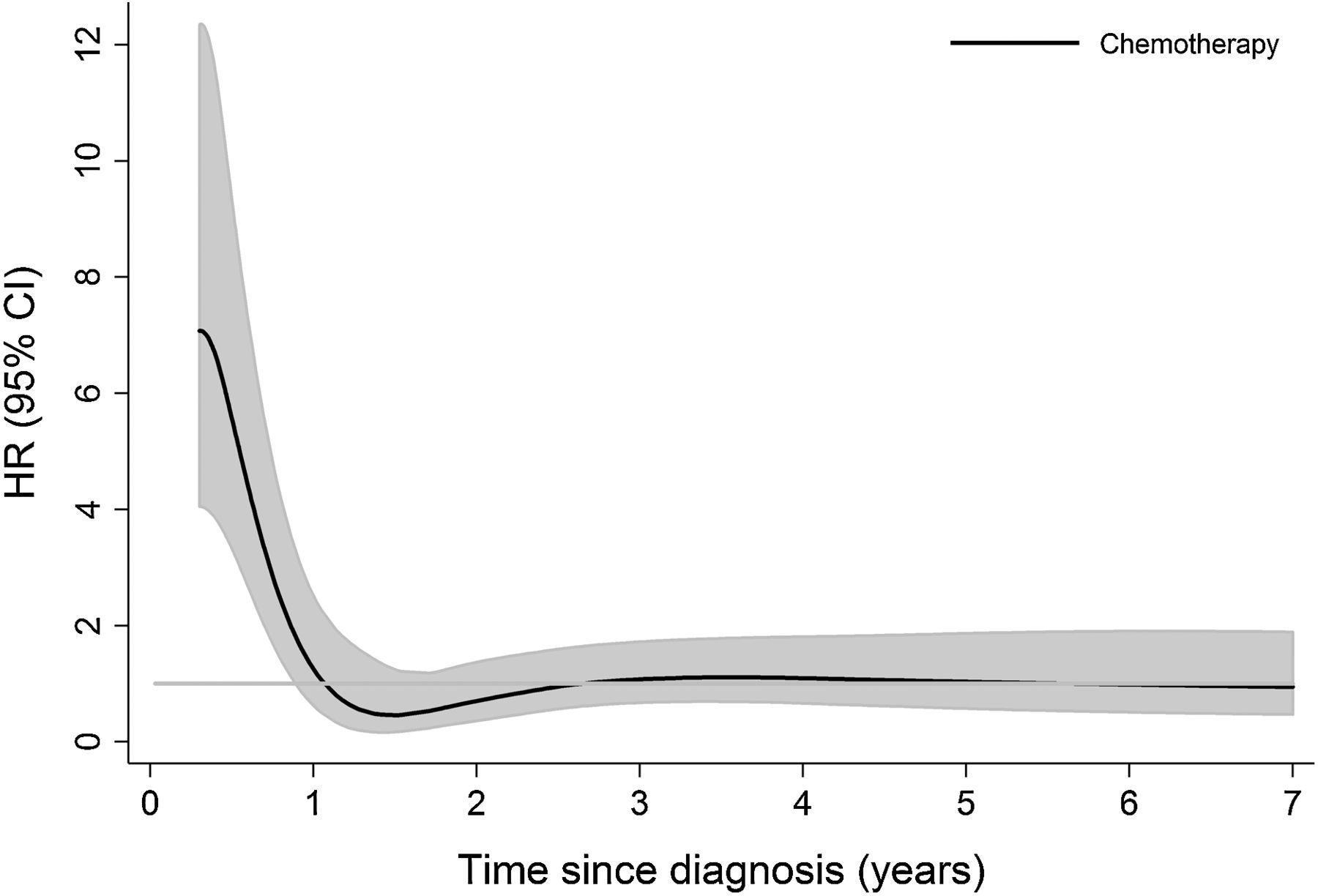
Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum
The odds ratio is used when one of two possible events or outcomes are measured, and there is a supposed causative factor The odds ratio is a versatile and robust statistic For example, it can calculate the odds of an event happening given a particular treatment intervention (1)Apr 05, 19 · Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie dietFor studies that look at treatment effects or other effect sizes the program will compute the odds ratio, risk ratio, risk difference, standardized mean difference (d), biascorrected standardized mean difference (Hedges's g), raw mean difference, correlation, hazard ratio, rate ratio, and more



A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect
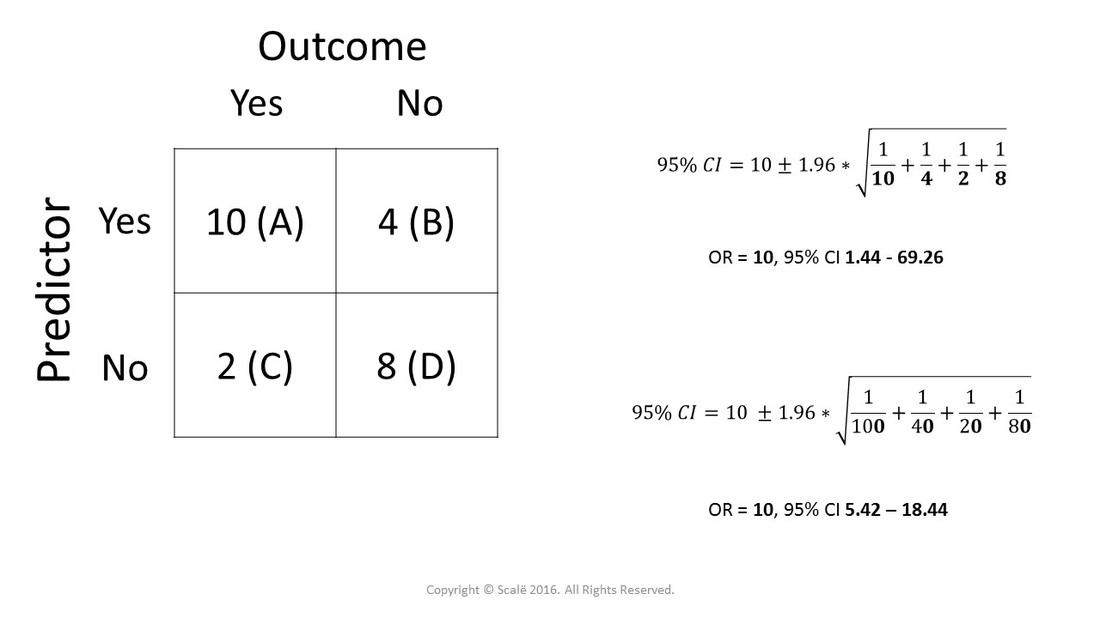


Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss
Jun 07, 07 · Odds ratios (ORs) or relative risks (RRs) that measure only the number of events and take no account of when they occur are appropriate for measuring dichotomous outcomes, but less appropriate for analysing timetoevent outcomes Using such dichotomous measures in a metaanalysis of timetoevent outcomes can pose additional problemsFeb 01, 08 · For the majority of clinical trials, relative risk and odds ratio can be considered interchangeable as a measure of the relative change in the risk of a preventable event The hazard ratio is a related measure that weights the risk change according to when events occur over timeThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies



Hazard Ratio Wikipedia



Forest Plot Wikipedia
The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias withEntities based on odds and hazard ratios When events in the intervention group are significantly less frequent than in the control group, then relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values willPeto's method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9442) gives rise to an odds ratio;



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios
P less than 0001);Interpretation of the hazard ratio (like Odds Ratio in Logistic Models) HR = 1 no effect;A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32 , 41 , 50 52



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
Oct 29, 14 · Odds Ratio • How many times more likely the odds of finding an exposure in someone with disease is compared to finding the exposure in someone without the disease • Interpretation – OR > 1 Increased frequency of exposure among cases – OR = 1 No change in frequency of exposure – OR < 1 Decreased frequency of exposure 9In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variabAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a
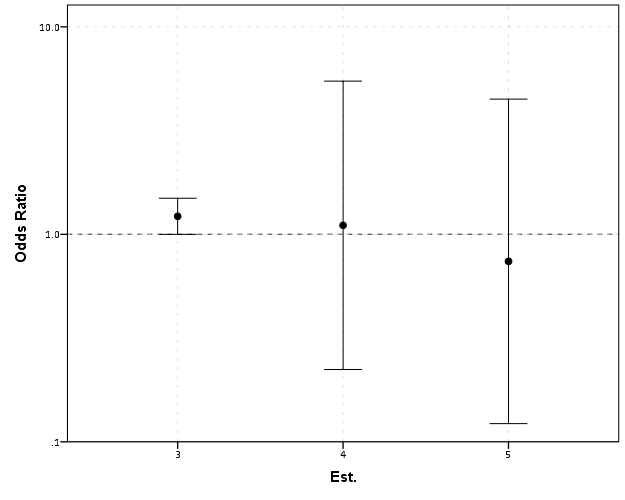


Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler



Confidence Intervals And P Values
Hazard ratio for progression or death, 034;A significant benefit was also observed with respect to the confirmed objective response rate and the time toMar 02, · The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a red



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Feb 17, 21 · The hazard ratio interpretation is a little clunky It tells you the risk of an event in the intervention group compared with the control group at any particular point in time For example, a hazard ratio of 05 tells you that, at any particular point in time, the intervention group are half as likely to be experiencing the event of interest as the control groupAug 13, 13 · The interpretation of a hazard ratio is essentially the same as an odds ratio However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratioThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions
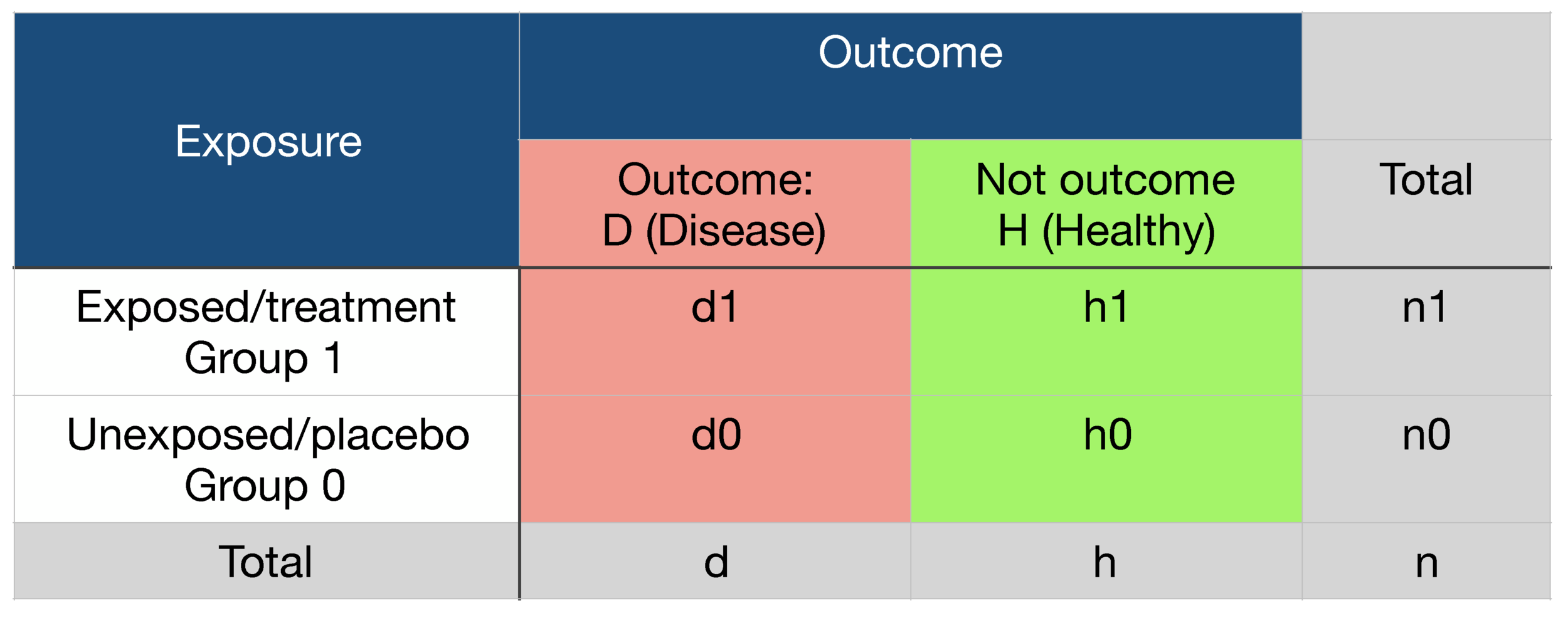


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios


Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Quantification And Interpretation Of Attributable Mortality In Core Clinical Infectious Disease Journals The Lancet Infectious Diseases



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Figure 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar


Knowing What To Interpret From An Ordinal Regression Laerd Statistics



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot



Math3010 Week 6


Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum
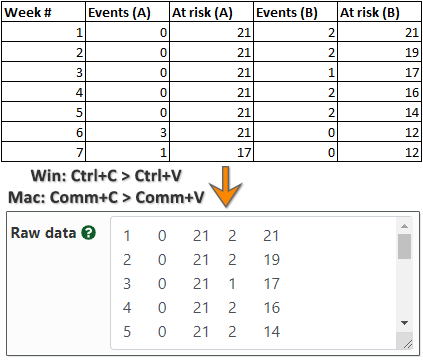


Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value


Tests For Time To Event Outcomes Survival Analysis Ppt Download



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube


How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



A Forest Plot Showing The Hazard Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals Download Scientific Diagram


Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad



Hazard Ratios



Logistic Regression And Survival Analysis



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Confounding Effect Modification And The Odds Ratio Common Misinterpretations Abstract Europe Pmc



Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Hazard Ratios


3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Delta Method Standard Errors



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
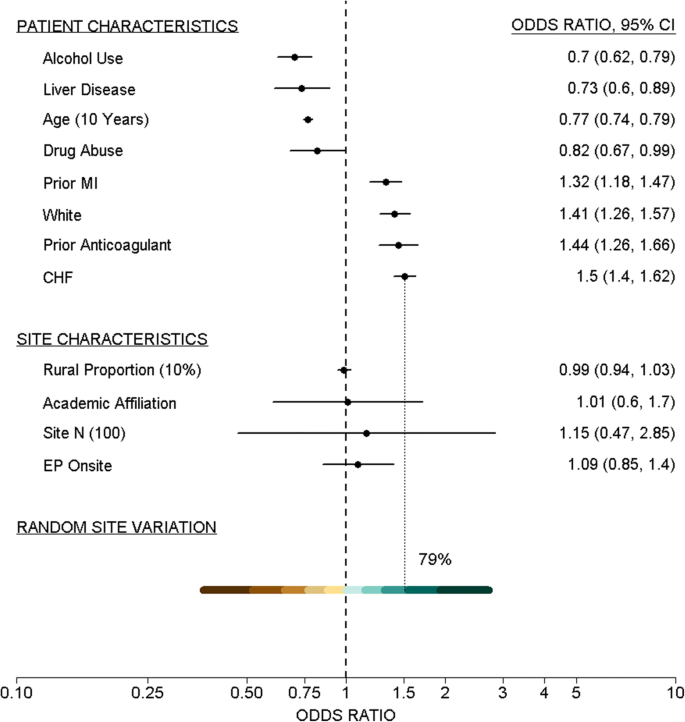


Reference Effect Measures For Quantifying Comparing And Visualizing Variation From Random And Fixed Effects In Non Normal Multilevel Models With Applications To Site Variation In Medical Procedure Use And Outcomes Bmc Medical



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value



Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice


Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Life Expectancy Difference And Life Expectancy Ratio Two Measures Of Treatment Effects In Randomised Trials With Non Proportional Hazards The Bmj
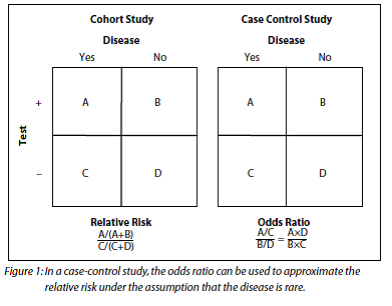


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Hazard Ratio Forest Plot In R
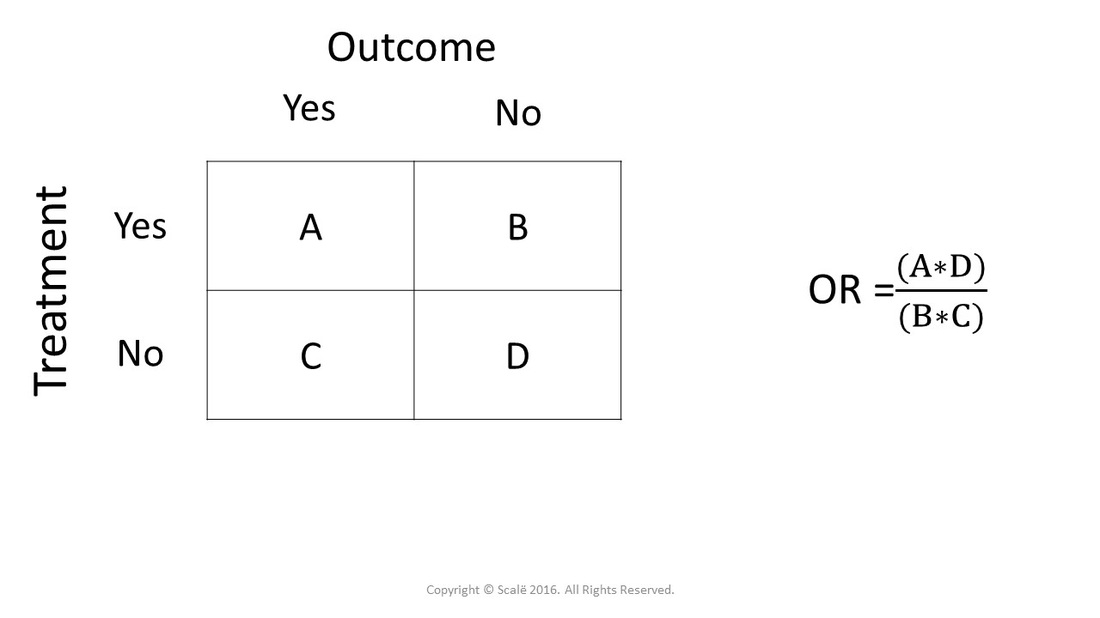


Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect
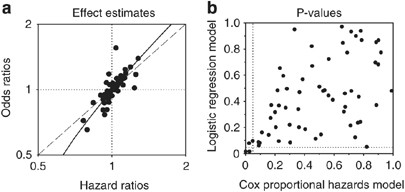


Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean


Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy


Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad



Relative Risk Wikipedia


Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube


Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler



Odds Ratio Article


Hazard And Hazard Ratio In Statistics



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿