07 · The complete nutritional value can be determined for per 100 grams of pulp as Calcium mg, potassium 375 mg, vitamin A 15 IU, Thiamine 016mg, Tartaric acid 38mg, Phosphorous mg, protein 310g, magnesium 92 mg, Riboflavin 007mgIts young leaves also contain multiple nutritional benefitsIt is packed with lots of nutrition that helps to promote health and manage some health conditionsFelker and Clark, 1980) 2212 Worldwide importance and economic value Tamarind is economically valuable and multipurpose insofar

9 Tamarind Lost Crops Of Africa Volume Iii Fruits The National Academies Press
What are the benefits of tamarind leaves
What are the benefits of tamarind leaves- · Tamarind leaves possess anti inflammatory properties and can be used as cure for joint pains and other inflammations 9 Protects The Body From Infections Tamarind leaves are a storehouse of Vitamin C, which wards away any microbial infections, leading to a healthy bodyTamarind fruit benefits are unique as it is a natural remedy for your eyesight, reduce your joints inflammation, reduce hair loss, improve your diabetes condition, and is excellent for your heart Click here to find out why so many people like tamarind fruit and what are its real health benefits
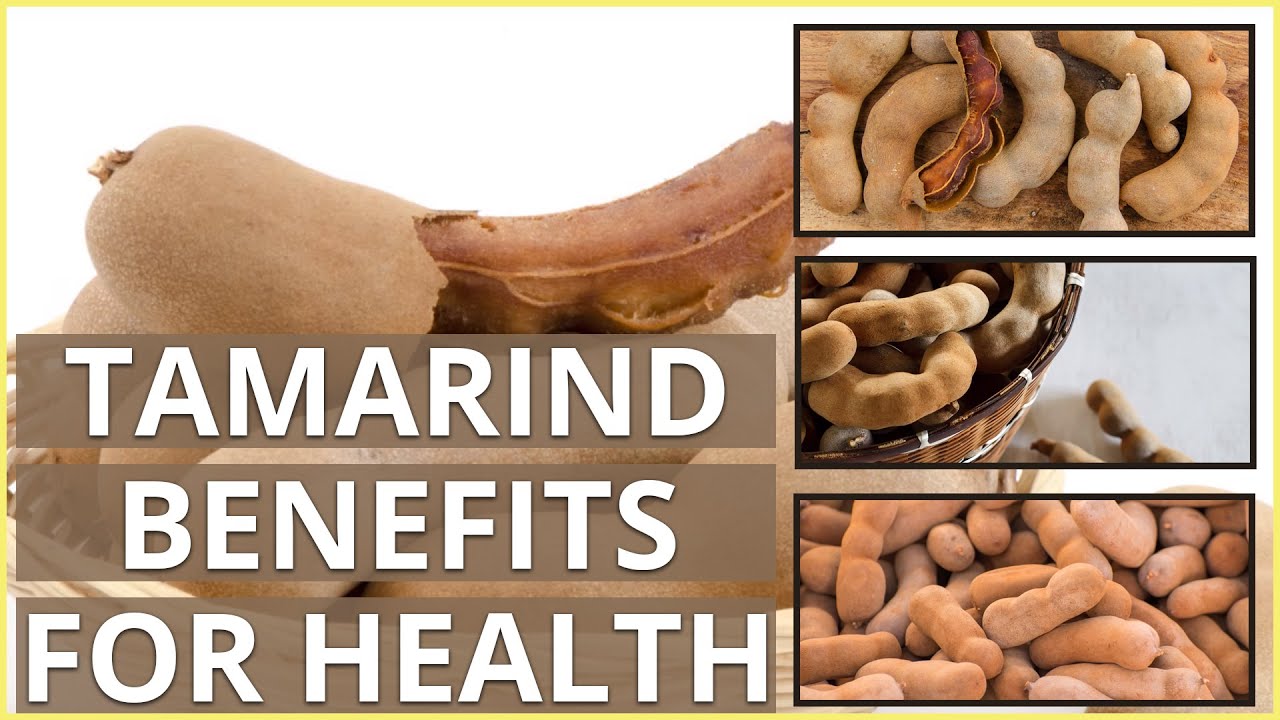


10 Amazing Tamarind Benefits For Health Youtube
The tamarind (Tamarindus indica L) is a usually evergreen legume tree It grows slowly, up to 2530 m high, and can live as long as 0 years Leaves are compound, divided in 1018 opposite and oblong leaflets Orangeyellow or pinkish flowers are grouped in racemes Fruits occur 712 years after sowing They are rustycoloured pods, 1018 cm long x 2 cm broadOrganic matter 975 and 9;Black velvet tamarind is an indigenous fruit also known as African velvet tamarind, it is without any adverse reaction and is been eaten by all ages because it is a kind of vitamin C supplement The fruit inside the shell is either dried or pulpy with taste sweetsour;
2213 Culinary uses, nutritional value and health benefits Tamarind fruit pulp has many uses indomestic and industrial food and medicine and isconsidered the most valuable part of the treeTamarind is also a rich source of many essential vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin C, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid It provides good amounts of minerals like copper, calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, selenium and zincTamarind (Tamarindus indica L) belongs to the dicotyledonous family Fabaceae (Leguminosae), and the genus Tamarindus is monotypic The tree is a longlived, large evergreen, and generally grows wild A mature tree may attain a maximum height of 30 m Leaves are pinnate with opposite leaflets, giving a billowing effect in the wind, and consist
A proximate analysis carried out by Nicholas on the nutritional value of velvet tamarind shows that it contains;* The % Daily Value (DV) tells you how much a nutrient in a serving of food contribute to a daily diet 2,000 calories a day is used for general nutrition advice Add to food diary Add to comparison Add to meal Add to favorites Download spreadsheet (CSV) Badges low fat, high sugar Tamarinds, raw nutrition facts and analysis per serving Vitamins;Tamarind Tamarindus indica Nutritional characteristics Table 2 presents some of the nutritional characteristics of principal tree fodders and shrubs The data has been assembled from various sources, but in particular Devendra (1979), NRC (1981), Kearl (19) and Devendra (1990b) In the absence of data on cell wall contents, the average crude fibre level is indicated



Effect Of Tamarind Tamarindus Indical Seed On Antioxidant Activity Phytocompounds Physicochemical Characteristics And Sensory Acceptability Of Enriched Cookies And Mango Juice Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly



Pdf Leaf Nutrient Status And Fruit Yield In Different Age Classes Of Tamarind Plantation In Northern Tamil Nadu India
Manila tamarind is a multipurpose tree Its pods are edible and contain a thick sweetish acidic pulp They can be eaten raw or processed into a soft drink similar to lemonade Oil can be extracted from the seeds and is used for cooking or for making soaps Manila tamarind oil meal, pods and leaves are useful livestock feeds The byproduct of oil extraction is a proteinrich meal (30% protein) that can be fed to animals Pods are also relished by all classes of livestock and Manila tamarindDealt simply and solely with the nutritional and medicinal value of tamarind products For that reason, we decided to collect, document and compare detailed data on tradi tional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology for fruit pulp, seeds, leaves and flowers, and bark of the tamarind tree The literature search was done by using the following search terms 'tamarind'The tamarind tree produces rather inconspicuous flowers of a pale yellow colour or with red or orange streaks, Nutritional values The tamarind can boast elevated quantities of minerals (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium and selenium) and is an excellent source of vitamins A, B1, B2, , B5, B6, C, K, and J Along with a 31% water content, it consists of simple



Pdf Tamarind Tamarindus Indicus L Fruit Of Potential Value But Underutilized In Nigeria



Dialium Guineense Wikipedia
Nutrition Data's opinions and ratings are based on weighted averages of the nutrient densities of those nutrients for which the FDA has established Daily Values, and do not consider other nutrients that may be important to your health or take into account your individual needs Consequently, Nutrition Data's higherrated foods may not necessarily be healthier for you than lowerratedTamarind is a tree with miraculous benefits All its parts are used for a variety of health and medicinal purposes Right from the bark, to the leaves, to the flowers, to the fruits, each part of this tree has a role to play in maintaining our health It is a tropical tree · The leaves and bark, for instance, have been used to promote wound healing, bronchitis and inflammation of the eye A 15 study published in Scientific Reports also found that tamarind seed has antiarthritic properties and is able to decrease several markers of inflammation in the body In addition to tamarind, other antiinflammatory foods include turmeric, ginger, leafy



Tamarind A Functional Food For Improving Digestion Reducing Cholesterol And Lowering Blood Pressure Wisdom Of The Plant Devas



10 Amazing Tamarind Benefits For Health Youtube
Crude fat 54 and · Tamarind pulp is rich in nonstarch polysaccharides, the dietary fibre like gums, hemicelluloses, mucilage, pectin and tannins It is rich in tartaric acid which is a very powerful antioxidant Tamarind contains many volatile phytochemicals like limonene, geraniol, safrole, cinnamic acid, pyrazine, methyl salicylate and alkylthiazoles · USDA Zone 9b to 11 Difficulty Easy Other Names Tamarindus indica, tamarindo, tamarin, tamarinier, tamarinier des Indes, tamarindier, tamarinde, sampalok, asam jawa, ambli, imli, chinch, makharm Tamarind tree is native to Africa and grows like a wild plant in Indian subcontinent It's also grown across Southeast Asia, South America and tropical parts of
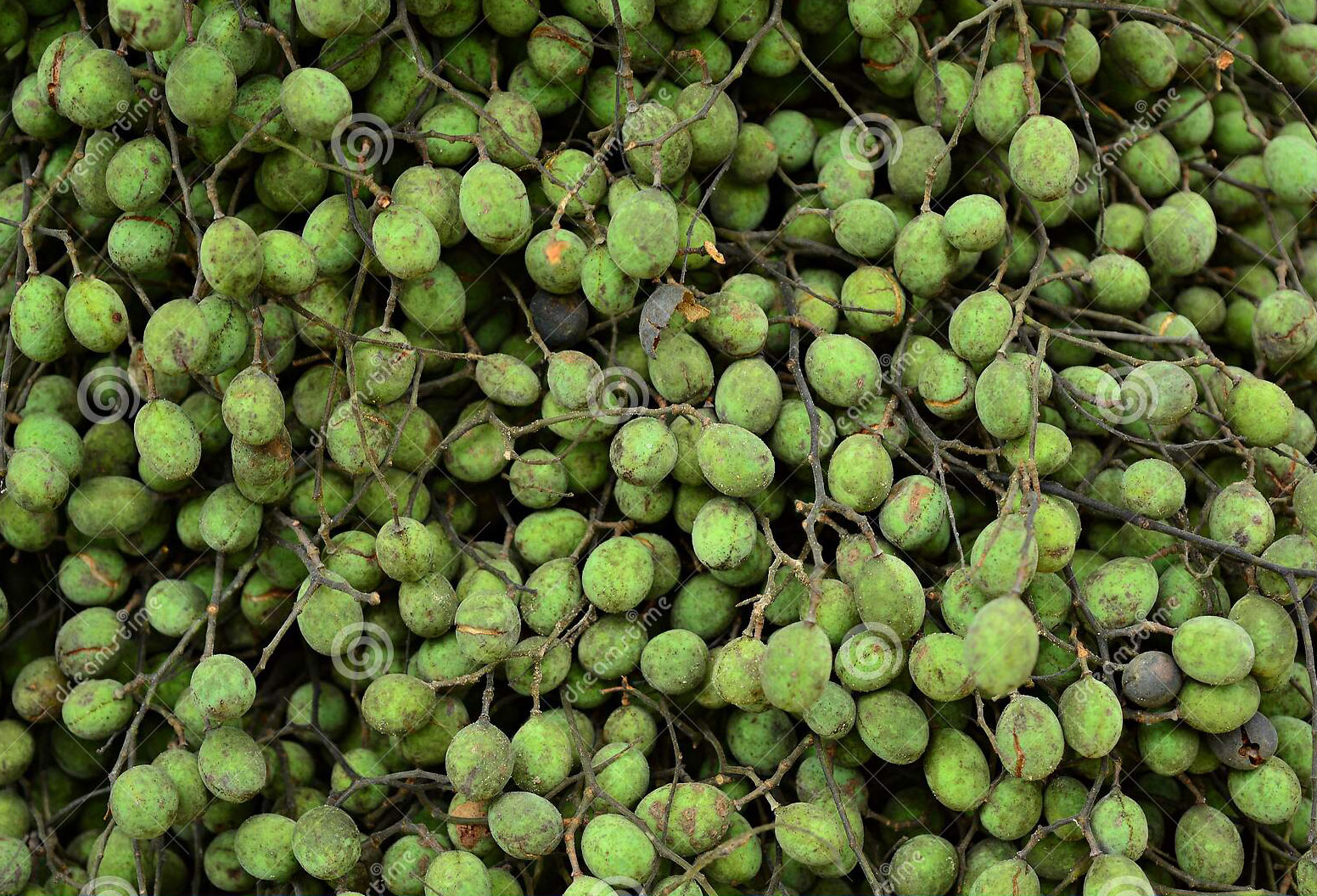



Velvet Tamarind Facts And Health Benefits



Pudina Mint Leaves Health Benefits Of Pudina Juice Uses For Skin Hair And Side Effects
Dry matter 941 and 951;Few plants will survive beneath a tamarind tree and there is a superstition that it is harmful to sleep or to tie a horse beneath one, probably because of the corrosive effect that fallen leaves have on fabrics in damp weather Some African tribes venerate the tamarind tree as sacred To certain Burmese, the tree represents the dwellingplace of the rain god and some hold the belief thatThe tamarind tree originates from Madagascar The most valuable and commonly used part is the fruit The pulp constitutes 3050% of the ripe fruit, the shell and fibre account for 1130% and the



Sassafras Wikipedia



9 Tamarind Lost Crops Of Africa Volume Iii Fruits The National Academies Press
· Nutritional Value Of Tamarind Due to its nutrional values and health benefits, Tamarind has been known as a very valuable commodity in the world The most wellknown nutrition contained within it are; · Tamarind Leaves Nutritional Value Health Benefits Uses SideEffects Cultivation Tamarind leaves has a myriad of benefits chief of them being providing relief from malaria Its medical benefit though is not confined to just that as it can also cure jaundice and diabetes, helps cure scurvy, treats ulcer, inhibits genital infections, protects the whole body from infections and · Tamarind has a protein content of 34 grams per cup;


Pdf Imlii A Craze Lovely



The Tamarind A Tree Well Traveled Family Travel Africa
Nutritional Value Tamarind leaves are an excellent source of vitamin A and vitamin C They also contain calcium, iron, fiber, and potassium Applications Tamarind leaves are commonly ground into a paste or dried and soaked in water to create a sour flavoring agent They can be added to soups, stews, dal, curries, chutneys, and rasam Tamarind leaves are also cooked with the · Tamarind also contains a lot of vitamins and minerals Out of the recommended daily dosage for each of the following, tamarind has 4% of vitamin C, 5% of vitamin B6, 7% of calcium, 22 % of iron, 26% of magnesium, 1% of zinc and 16%Leaves Tamarind leaves and flowers, dried or boiled, are used as poultices for swollen joints, sprains and boils Lotions and extracts made from them are used in treating conjunctivitis, as antiseptics, as vermifuges, treatments for dysentery, jaundice , erysipelas (a skin infection that often follows strep throat) and hemorrhoids and various other ailments (Morton 1987)



17 Best Benefits And Uses Of Moringa Powder Coconut Health Benefits Moringa Powder Tomato Nutrition



The Health Benefits Of Herbal Medicine And Its Necessity Likhoon
· Manila Tamarind Health Benefits Manila Tamarind is a sour edible fruit mostly used for cooking, but also contains high nutritional value and numerous health benefits to the body Tamarind or Tamarindus indica is a leguminous tree came from an indigenous family of Fabaceae This plant can be usually found in tropical climate countries includingTamarind is going to solve all your abdominal issues In traditional medicine, tamarind has been used as a laxative because it contains tartaric acid, malic acid, and potassium While the fruit is used to relieve constipation, the leaves are used to treat diarrhea, and the root and bark are taken to alleviate abdominal pain 1 2These kinds of compounds with a high value not only as nutrient but also as antioxidant and antimicrobial /26,27/ were reported in previous papers in India and Pakistan /28,29/, but never in tamarind trees growing at the American continent As well as these previous studies, C 160 , and C 18n , appear as the main fatty acids in tamarind leaves, but also the long chain fatty acid Methyl


Is Tamarind Keto 5 Benefits And How To Use It Perfect Keto



Sita S Ruchulu Vankaya Chintachiguru Kura Eggplant With Tender Tamarind Leaves
· The tamarind tree has the capability to withstand long periods of drought because of its deep tap rooting and extensive lateral rooting system, and also the ability to grow in poor soils because of their nitrogen fixing property (Felker, 1981;0716 · Trace amounts of vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), folate, vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), copper and selenium It also contains 6 grams of fiber, 3 grams of protein and 1That's 7 percent of your daily value (DV) For optimal health, 10 to 30 percent of your daily caloric intake should come from protein, which is needed to build tissue including bones, skin and muscles



Physicochemical Composition Of Tamarindus Indica L Tamarind In The Agro Ecological Zones Of Uganda Okello 18 Food Science Amp Nutrition Wiley Online Library



Seven Wonders Garden Tamarind Tree 2
2509 · Tamarind is not a significant source of vitamin D, so you will need to get it from other sources Nutrition Tamarind is very rich in nutrients, providing at least 10% of VitaminThe report states that the fruit is rich in minerals (magnesium, sodium, iron, potassium and carotene (Vitamin A), copper), sugars and tartaric acid, citric acid, malic acid, ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) and Niacin As anticipated, this fruit also has high levels of antioxidants5865% carbohydrates, 394% proteins, 534% crude fat, 143mg/100g iron, 40mg/100g magnesium, 2mg/100g sodium, 35mg/100g calcium, 121mg/100g potassium, 1053% moisture, 1250% ash and 105% ash Outside the fruit, the leaves and bark of the Awin tree


Benefits Of Tamarind



Mexican Tamarind At The Rancho En M Wikipedia Org Wiki Ta Flickr
2513 · Tamarind leaf pulp contains pipecolic acid, nicotinic acid, 1malic acid, geraniol, limonene, pipecolic acid, lupanone, lupeol, orientin, isoorientin, vitexin, isovitexin, cinnamates, serine, pectin, tannins, and glycosides Tamarind fruits commonly contain tannins, succinic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, and pectin Its seeds contain campesterol, betaamyrin,Nutrition Facts for Moringa, a Superfood from the Himalayas Known as the Miracle Tree in India, Moringa oleifera or drumstick tree is native to the Himalayan and North African mountains Because it grows fast and the leaves retain lots of nutrients when dried into powder, moringa has been used in India and Africa to fight malnutritionTamarind has about 239 calories per 100 gm of weight How to Buy Tamarind Tamarind is available as dried pods, pressed fibrous slabs, tamarind blocks, readytouse slices, concentrates, balls or in the paste form It is best to buy tamarind pulp or paste since it becomes more convenient while cooking, compared to boiling pods



Taro Wikipedia



8 Evidence Based Health Benefits Of Papaya
Crude protein 157 and 42;How to Grow a Tamarind Tree Tamarind trees (Tamarindus indica) grow up to 100 feet tall and can live for over 0 years The tree has a short trunk withAnalysis was done to find out the composition and the nutrition value of the fruit Nutrients of black velvet tamarind Further, Journal of Food Biochemistry published that the composition of black velvet tamarind's seed and pulp respectively is listed as follows Moisture 59 and 49;



Here S How To Make The Healthiest And Yummiest Tamarind Juice Tastessence



Tamarind Nutritional Value Health Benefits Recipes
Velvet tamarind comes under the Leguminosae family which is tall, growing under tropical climatic conditions and also bears fruits The fruits are similar to the grapes and are consumable containing hard shells which must not be consumed Since the fruit contains tamarind flavor it has its English name as tamarind Taste is both sweet and sourTamarind is a longbean like pod grown on a longlived, mediumgrowth bushy tree, reaching a height of 121 to 1 meters The name tamarind has been derived from the Arabic term 'tamar' which means a 'dry date fruit' The fruit is native to tropical Africa, especially Sudan, Cameroon, Nigeria and Tanzania Today, it is cultivated throughout the tropical belt, right from Africa toNutritional Value of Velvet Fruit According to Gnansounou et al (14), Velvet tamarind has a potential for micronutrients (Gnansounou et al, 14) Like the other fruits, it emerges that the fruit pulp of velvet tamarind is rich in minerals with interesting values Iodine (0434 ± 012 mg/100 g) Iron (1475 ± 025 mg/100 g)
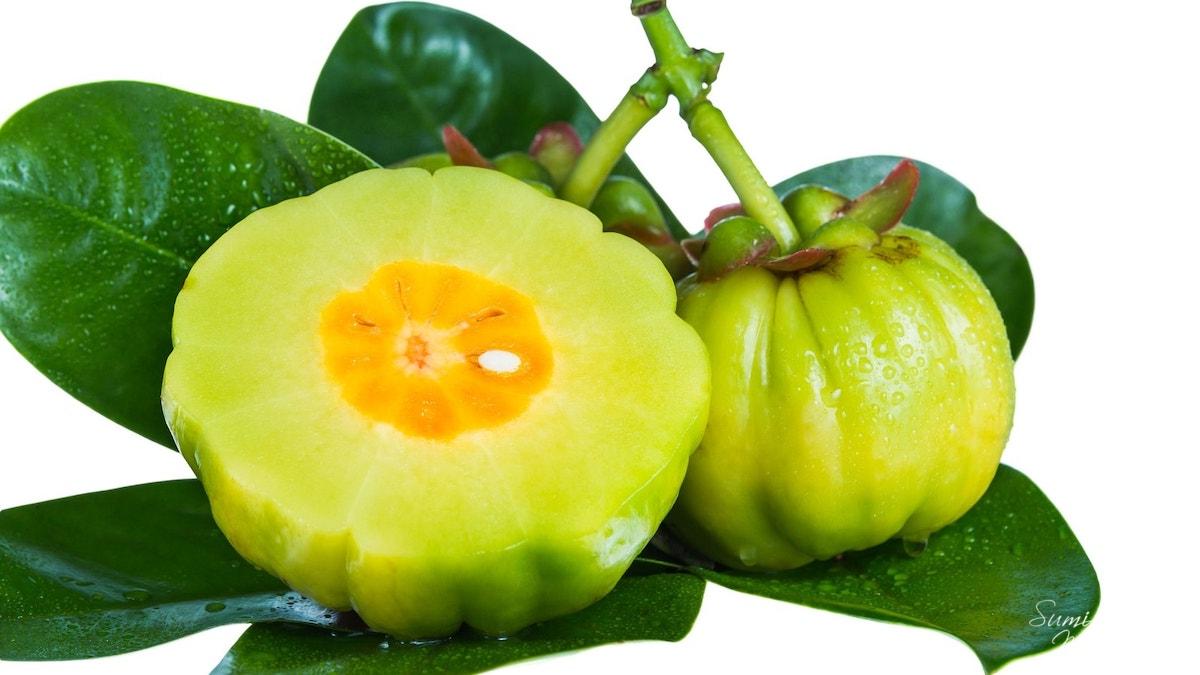



Health Benefits Of Cambodge Great Malabar Tamarind Benefits



Moringa Oleifera Moringa Oleifera Moringa Moringa Benefits
Important values in 100 grams of TAMARIND LEAVES tender like energy, moisture, protein, fat, carbohydrates, fibre, calcium, Iron and PhosphorusNutritional Value of Manila Tamarind Energy 78 kcal Water 778% Protein 3% Fat4% Carb 1% Fiber 12% Ash6% Calcium (13% RDI) 13 mg Phosphorous (42% RDI) 42mg Iron (27% RDI)5mg Sodium 19mg Potassium (63% RDI) 222mg Vitamin A 15mg Thiamin/B1 (166% RDI)24mg Riboflavin/B2 (58% RDI)10mg Niacin/B6 (3% RDI)60mg Vitamin C (221% RDI)



Spicytamarind How To Use And Store Curry Leaves



12 Health Benefits Tamarind Aids Weight Loss And Improves Nerve Function



34 Best Tamarind Health Benefits Ideas Tamarind Tamarind Health Benefits Health


Tamarind Wikipedia



Frequencies Of Year Round Tamarind Leaf And Fruit Consumption 1 Download Scientific Diagram
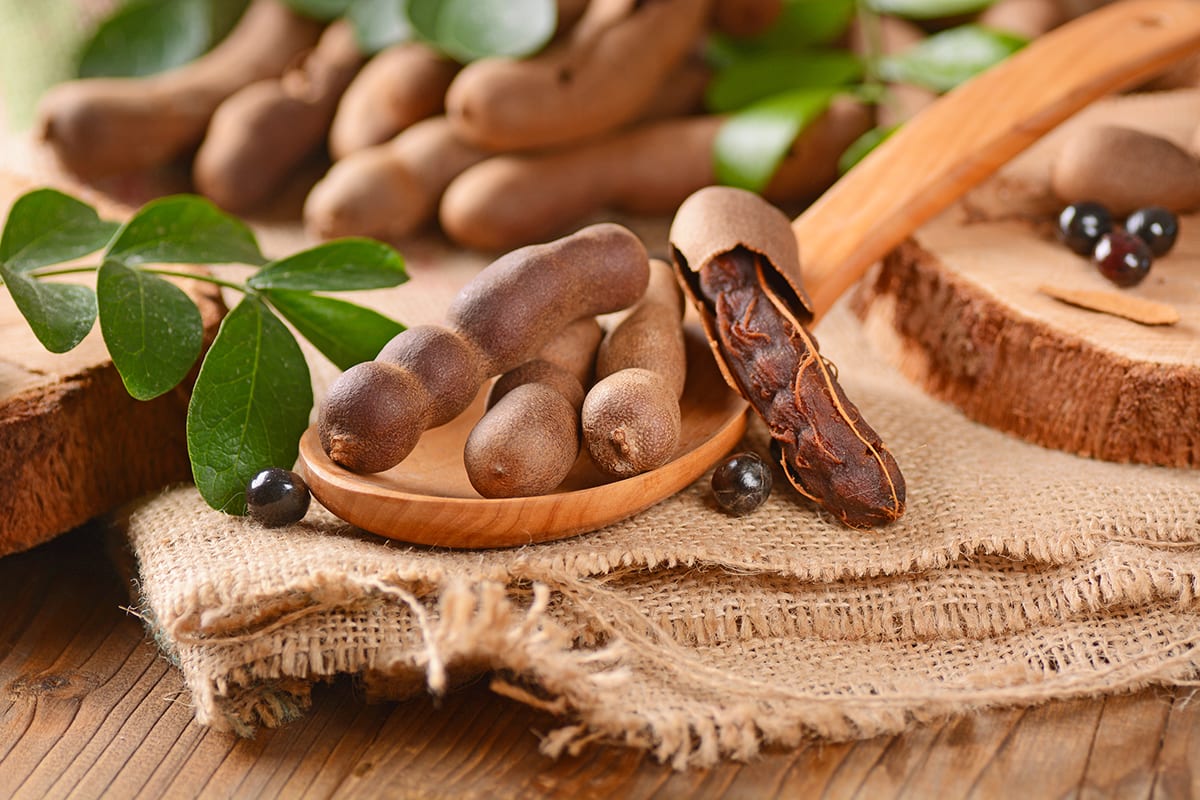



The Rich History Flavor And Health Benefits Of Tamarind



In Vitro Assessment Of The Nutritive Value Of Mixtures Of Leaves From Tropical Fodder Trees Semantic Scholar



Tamarind Juice Recipe Healthier Steps


Nutritional Values Benefits And Uses Of Garcinia Gummi Gutta



9 Tamarind Lost Crops Of Africa Volume Iii Fruits The National Academies Press



Acacia Seed Proteins Low Or High Quality A Comprehensive Review Adiamo Comprehensive Reviews In Food Science And Food Safety Wiley Online Library



Carrot Wikipedia



Tamarind Fruit Benefits Dr Axe Fruit Benefits Tamarind Fruit Tamarind



Taro Leaves Facts Health Benefits And Nutritional Value



What S Your Favourite Tree International Tree Foundation


Pdf Knowledge Attitudes And Practices In Tamarind Tamarindus Indica L Use And Conservation In Eastern Uganda



Tamarindus Ind En By Bioversity International Issuu



The Rich History Flavor And Health Benefits Of Tamarind



Pdf Tamarind Tamarindus Indica L In The Traditional West African Diet Not Just A Famine Food



Pdf Chemical Constituents Of Tamarindus Indica L Leaves



Pdf Nutritional And Anti Nutritional Value Of Tamarind Fruit Tamarindus Indica
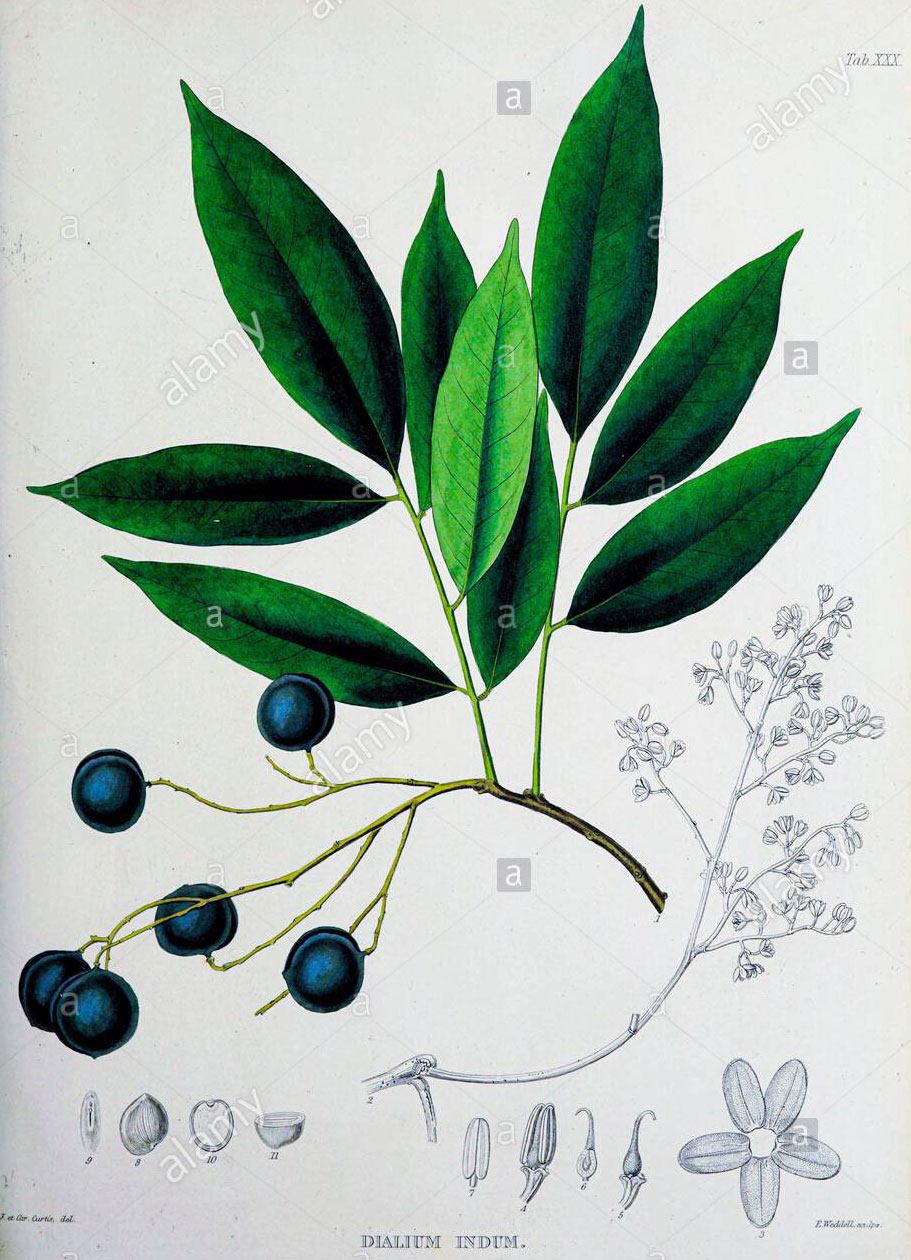



Velvet Tamarind Facts And Health Benefits


Is Tamarind Keto 5 Benefits And How To Use It Perfect Keto



Breadfruit Wikipedia



Distribution Biomass And Local Importance Of Tamarind Trees In South Western Madagascar Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
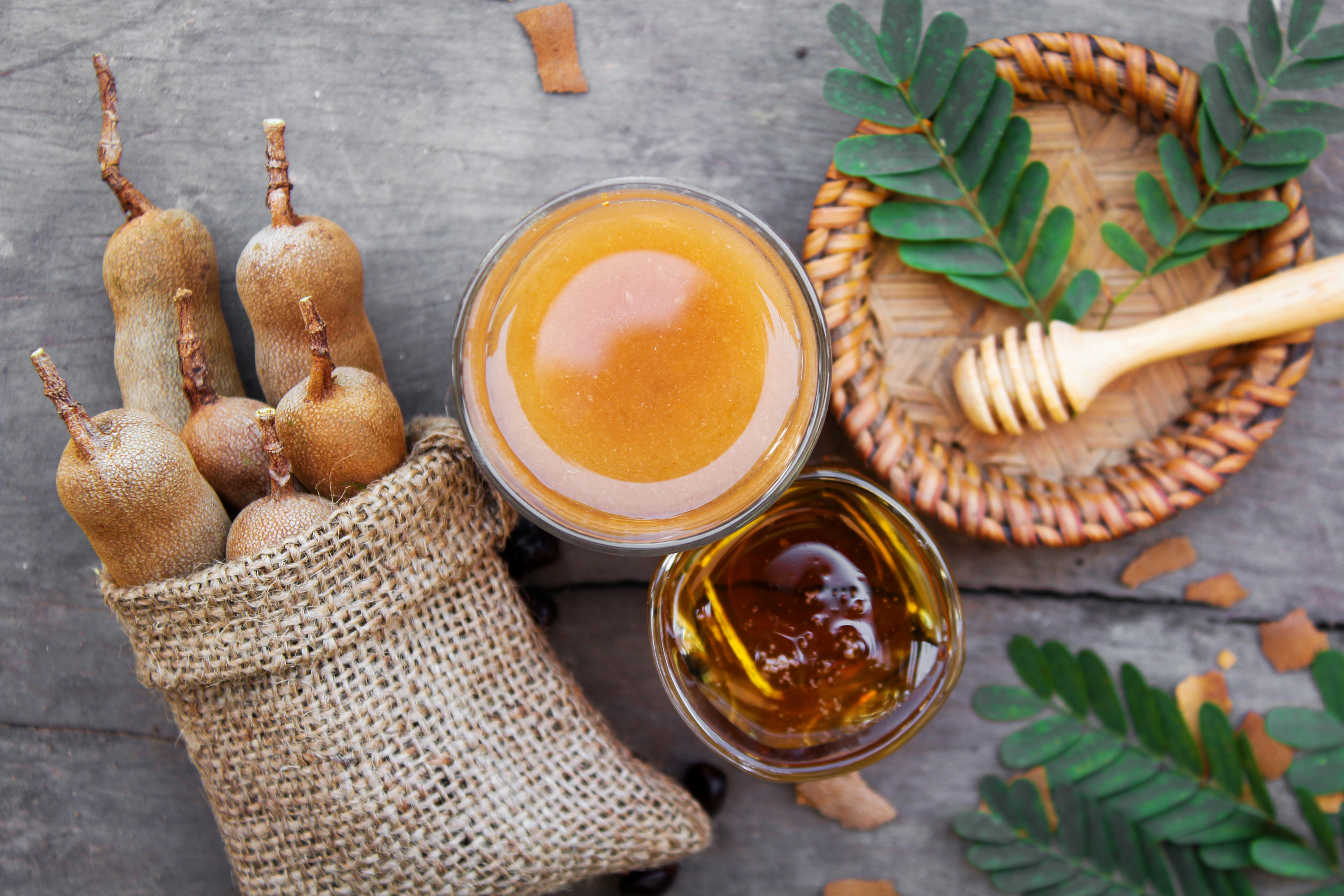



3 Promising Health Benefits Of Tamarind How To Eat It Selfhacked



Amazing And Interesting Food Facts Tamarind Tamarindus Indica Medicinal Properties Of Tamarind Seed Leaves Bark Health Benefits For Fever Cold Burns Rheumatism Digestive Disorders Scurvy Piles And Sore Throat With Side



Physicochemical Composition Of Tamarindus Indica L Tamarind In The Agro Ecological Zones Of Uganda Okello 18 Food Science Amp Nutrition Wiley Online Library



Sweet Tamarind Fruit Garden Weird Fruit Fruit Plants


Tamarind Juice Recipe Healthier Steps



Drumstick Health Benefits Nutrition Uses Recipes And Side Effects



Top 10 Wonderful Health Benefits Of Jasper Stone Fruit Benefits Tamarind Fruit Tamarind



Legume Definition Examples Britannica



9 Tamarind Lost Crops Of Africa Volume Iii Fruits The National Academies Press



Tamarind Tamarindus Indica Feedipedia



Tamarind Leaves With Dry Fish Gravy Andhra Style How To Make Mom S Recipes Handbook
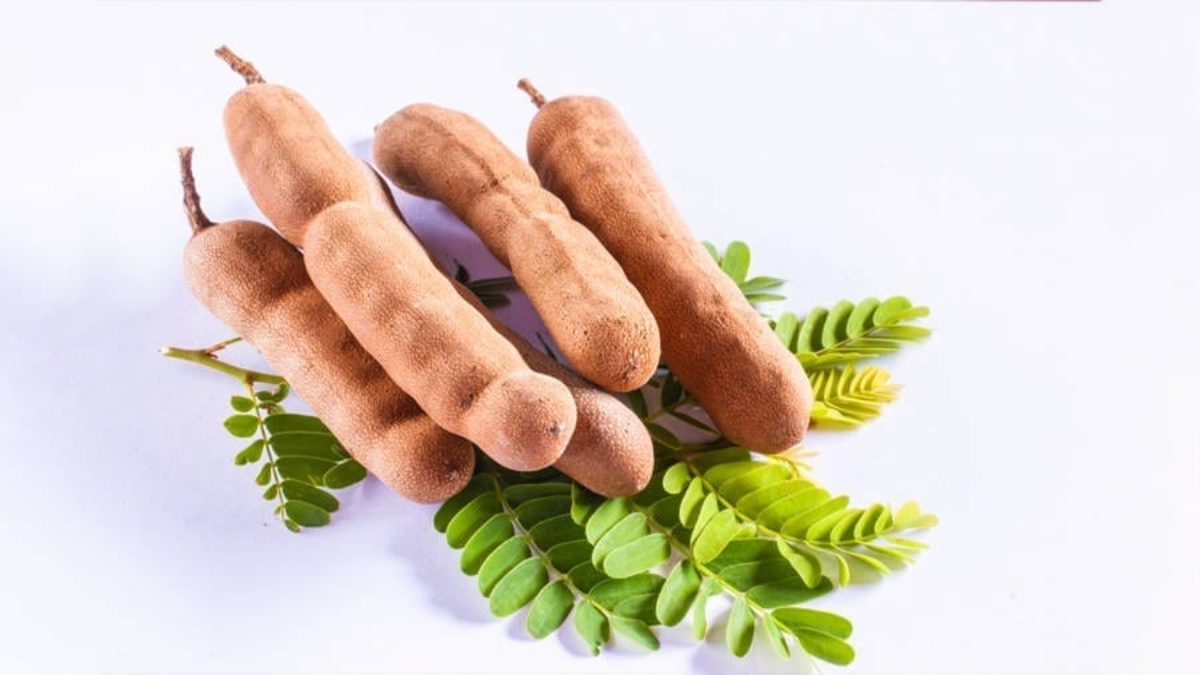



10 Benefits Of Tamarind For Your Health Meditative Mind



Tamarind Leaves With Dry Fish Gravy Andhra Style How To Make Mom S Recipes Handbook



Pdf Tamarind Tamarindus Indica L Research A Review



Pdf Antioxidant Capacity And Total Phenolic Content Of Fresh Oven Dried And Stir Fried Tamarind Leaves



Tamarindus Indica And Its Health Related Effects Topic Of Research Paper In Chemical Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub



Noni Leaves Information And Facts



Papaya Leaves Information And Facts



Pandan Leaves Information Recipes And Facts



29 Best Tamarind For Skin Ideas Tamarind Tamarind For Skin Tamarind Benefits



9 Tamarind Lost Crops Of Africa Volume Iii Fruits The National Academies Press



Pdf Organoleptic Evaluation Of Products Formulated From Tamarindus Indica L Tender Tamarind Leaves Semantic Scholar



Tamarind A Functional Food For Improving Digestion Reducing Cholesterol And Lowering Blood Pressure Wisdom Of The Plant Devas



Plant A Tamarind Tree To Decorate Your Property Part 4 Final Garden Lovers
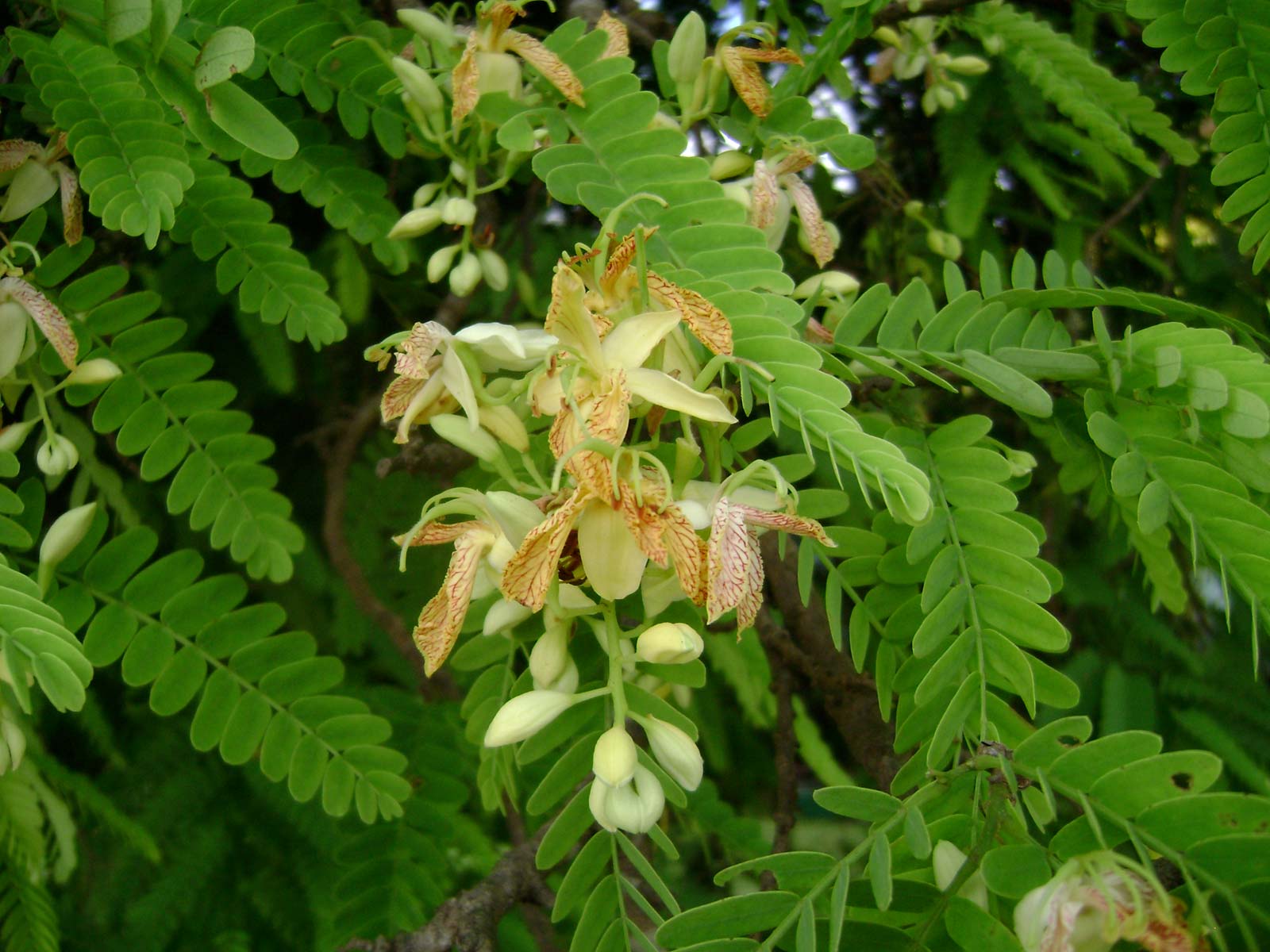



Tamarind Tamarindus Indica Feedipedia



Super Hero Moringa And Cinderella Tamarind By Nemani Chandrasekharnemani Issuu
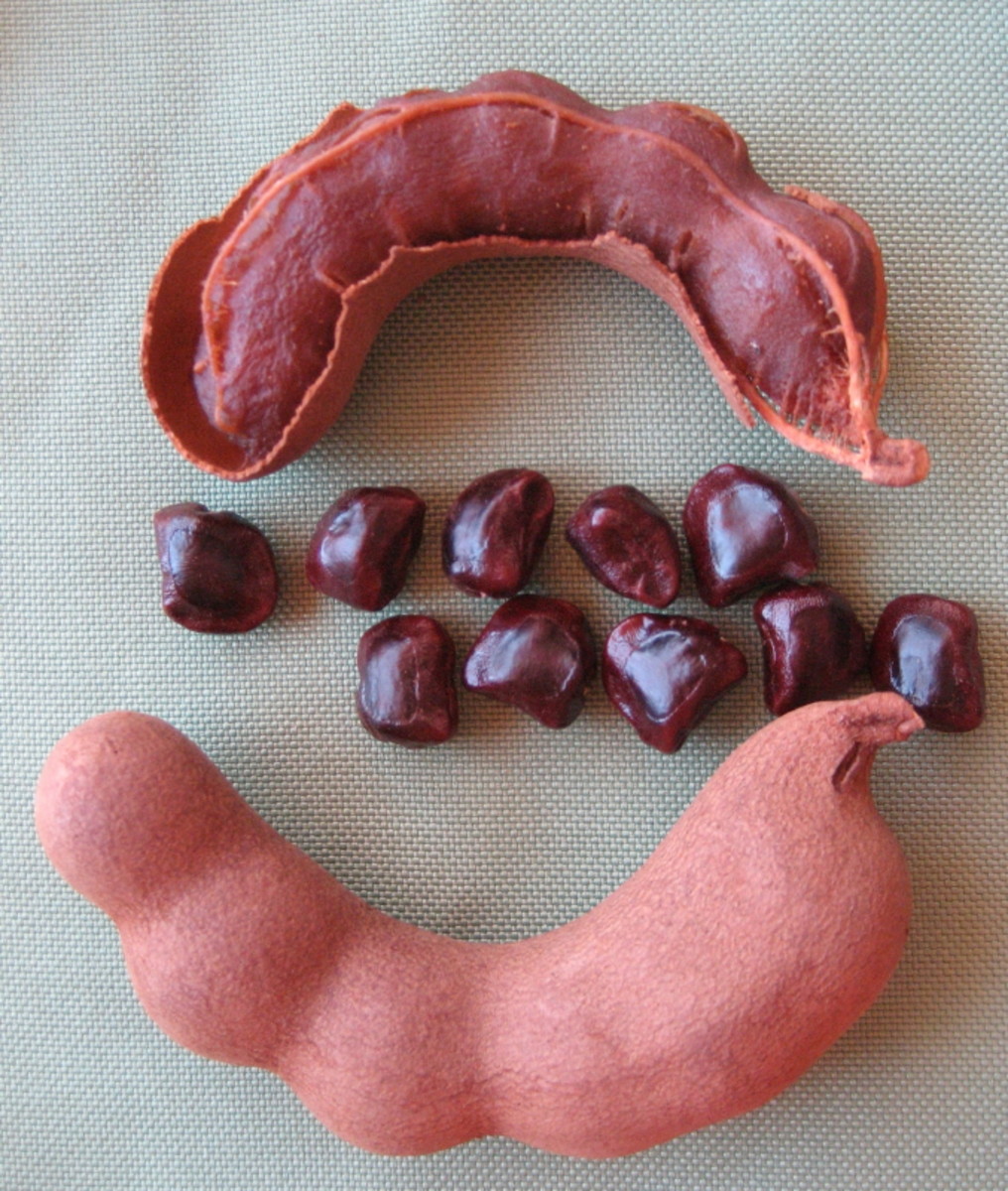



Health Benefits Of Tamarind Or Imli Hubpages



What Is Tamarind A Tropical Fruit With Health Benefits
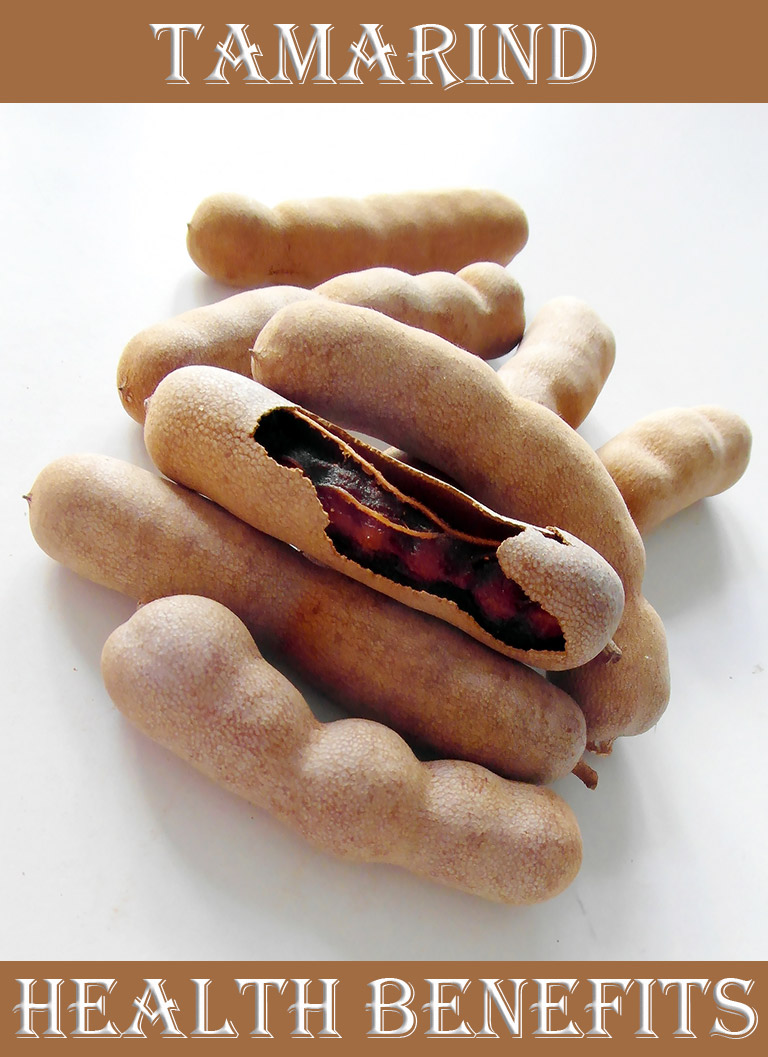



Health Benefits Of Tamarind A Tropical Superfruit



The Tamarind A Tree Well Traveled Family Travel Africa



Can Superfoods Boost The Planet S Health Too News Eco Business Asia Pacific



Spicytamarind How To Use And Store Curry Leaves



The Tamarind A Tree Well Traveled Family Travel Africa



Chinta Chiguru Health Benefits Tamarind Leaves Benefits Chinta Chiguru Health Tips Health Benefits Health



Top Health Benefits Of Tamarind Hb Times



11 04 6 47 Pm Angiephils Angiephils Beauty World Facebook
/tamarind_annotated2-f087a172cd7c451ab80da4b25b036f9b.jpg)


Tamarind Nutrition Facts And Health Benefits
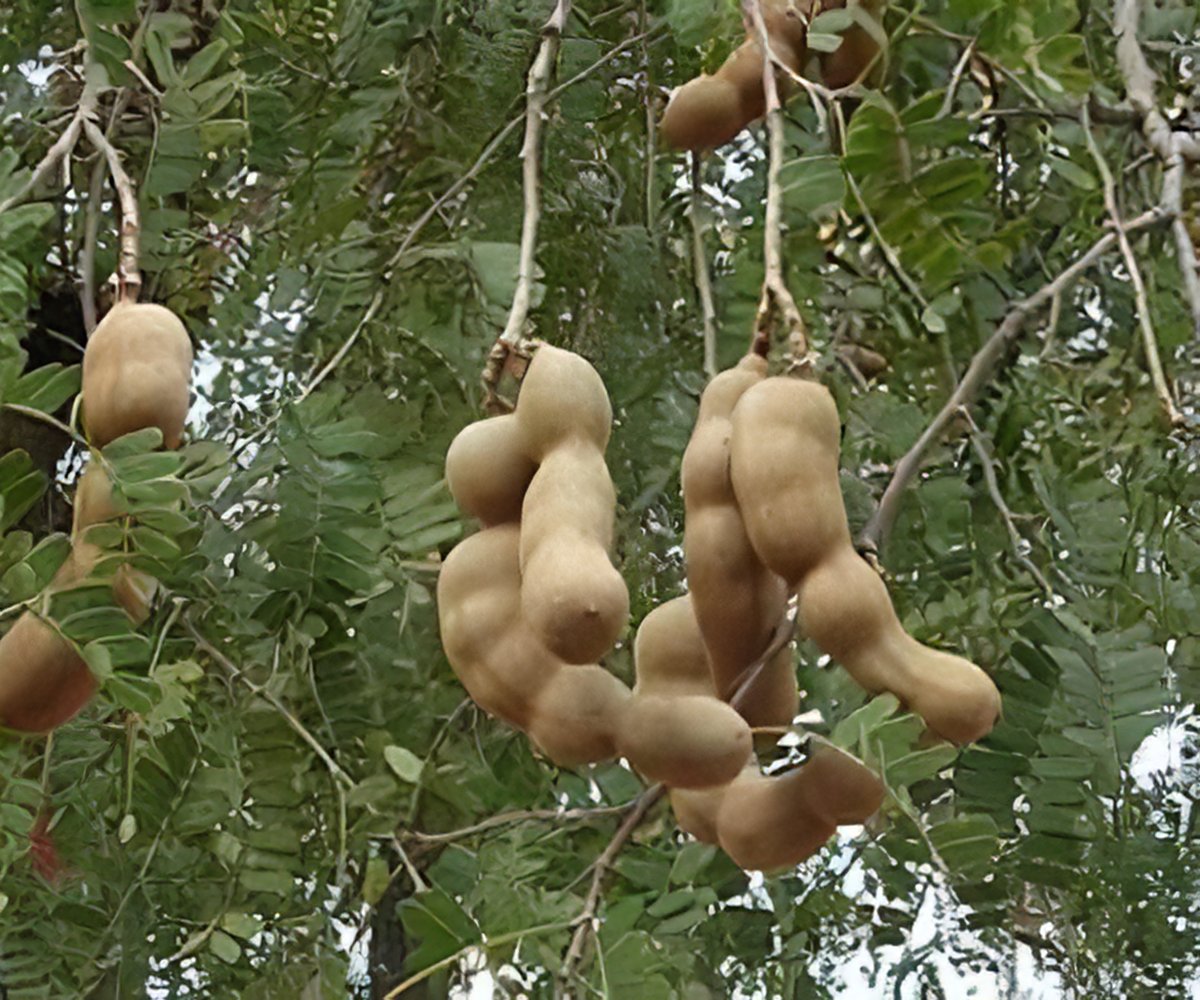



Tamarind Seeds To Regrow Damaged Nerves


Jujube Wikipedia



Tamarind Health Benefits The Nutrient Rich Superfood Hubpages



What The Hell Is Tamarind Anyway Huffpost Life



Tamarind Health Benefits The Nutrient Rich Superfood Hubpages



Tamarindus Indica Phytochemical Constituents Bioactive Compounds And Traditional And Medicinal Uses Springerlink



Top Health Benefits Of Tamarind Hb Times



Moringa Oleifera Leaf Extract Capsules Energy Booster Etsy Moringa Benefits Moringa Herbalism



Tamarind Tree Tropical Fruit Ripe Tamarind On Tree With Leaves Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿